Women go through a lot of changes in their bodies during and after pregnancy. The hormonal and biomechanical changes can increase load on the pelvic floor muscles, abdominal muscles as well as lower back structures. Such increase load, when not managed, can result in pain and aches that can persist as post-natal issue. Here are the common conditions pregnant ladies encountered and how physiotherapists can assist with preventing and managing its occurrence.

1. Lower back pain/ sacroiliac joint pain
Hormonal changes in the body relaxes ligaments to allow joints to loosen up in preparation for childbirth. The stability of joints, particularly in the lower back and pelvis, is compromised. As the baby grow, the weight of your tummy increases, shifting the centre of gravity and changes your posture. These lead to instability as well as back and pelvic pain.
2. Incontinence
The weight of a growing baby will continually press on the pelvic floor. Pelvic floor muscles need to be strong enough to support the baby weight otherwise it will not be able to withstand the pressure and will result in urine leakage, particularly when extra stress is added such as when coughing, sneezing and laughing.
3. Diastasis Recti (abdominal muscle separation)
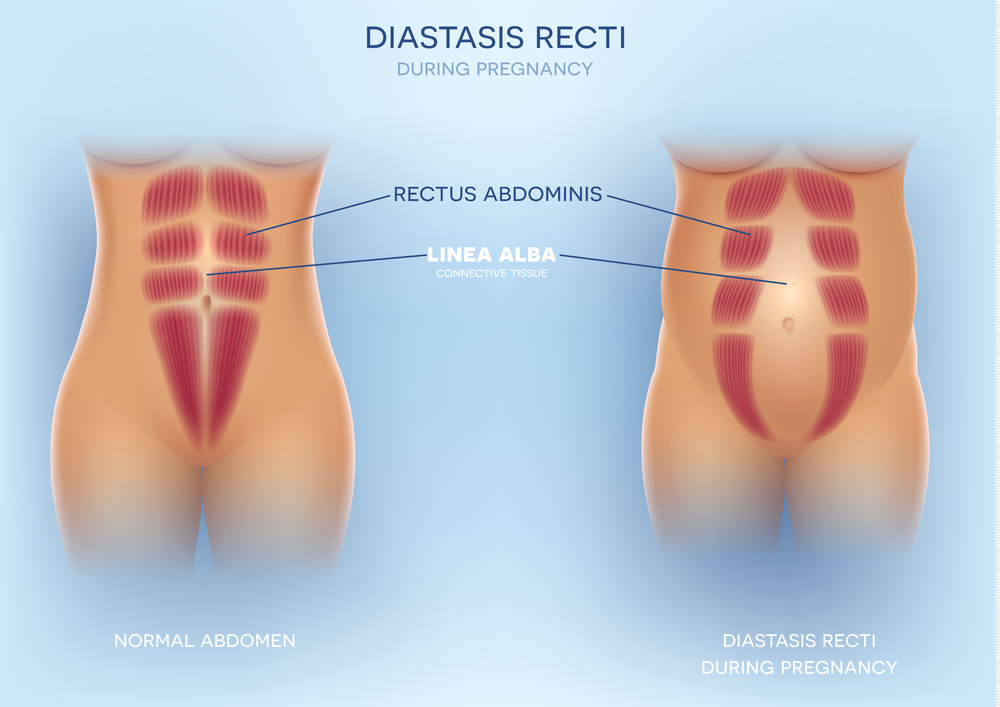
To make room for the growing size of a baby, your abdominal muscles are stretched and sometimes separation can occur where a gap can be felt. It is called diastasis recti and is commonly an issue later in pregnancy in the third trimester. Diastasis recti can reduce core strength postnatally which tends to rehab to assist recovery and regain strength.
4. Carpal tunnel syndrome
Fluid retention is another common problem during pregnancy. When fluid is retained on the peripherals of the arms, it can compress on nerve in the carpal tunnel, causing hand pain, tingling and numbness.
Our physiotherapists at Capital Physiotherapy are trained to assess and treat pregnancy related pain and issues. We can assist in managing your pregnancy by:
– Providing education regarding posture
– Assess and prescribe exercises according to your fitness level, with consideration of
your pain if there’s any, to strengthen your abdominal muscles and pelvic floor muscles. – Tape or advise on equipments (e.g. pregnancy belts) to support your lower back – Treatment to alleviate pain results from pregnancy related changes. – Advise on modifications to your activities to keep you active during pregnancy
Call us or make a booking online if you are experience pain or would like to condition for having a baby. At Capital Physiotherapy, our friendly physios are trained in clinical pilates to look after pregnant lady during and post-pregnancy.



 Commonly, manufacturers have advised to change your runners after 500-800 km; this is an extremely rough guide. While this figure has some use, we’re going to let you know of other signs that will help you find out if your shoes are still good to run in.
Commonly, manufacturers have advised to change your runners after 500-800 km; this is an extremely rough guide. While this figure has some use, we’re going to let you know of other signs that will help you find out if your shoes are still good to run in.

 Similarly, as you pound the pavement or the treadmill, the midsole of your shoe degrades over time. Here are the signs of when you should change your shoes:
Similarly, as you pound the pavement or the treadmill, the midsole of your shoe degrades over time. Here are the signs of when you should change your shoes: Hopefully that has helped you to find out when to change your running shoe. As much as we want to use the shoe until the upper is torn and your toes are showing, or the outsole is worn out completely, the truth of the matter is that your midsole will usually be the first to go.
Hopefully that has helped you to find out when to change your running shoe. As much as we want to use the shoe until the upper is torn and your toes are showing, or the outsole is worn out completely, the truth of the matter is that your midsole will usually be the first to go.

 With her wealth of clinical experience – in both public and private systems, Melanie is contactable at Capital Physiotherapy’s Hawthorn Physio clinic to provide you with the best physio treatment in the Hawthorn and for the surrounding suburbs.
With her wealth of clinical experience – in both public and private systems, Melanie is contactable at Capital Physiotherapy’s Hawthorn Physio clinic to provide you with the best physio treatment in the Hawthorn and for the surrounding suburbs.

